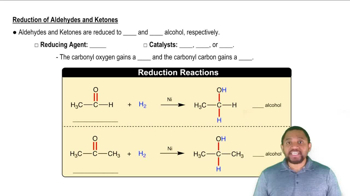
The carbonyl group can be reduced by addition of a hydride ion (H–) and (H+) a proton. Removal of H– and H+ from an alcohol results in a carbonyl group.
a. To which atom of the carbonyl is the hydride ion added and why?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: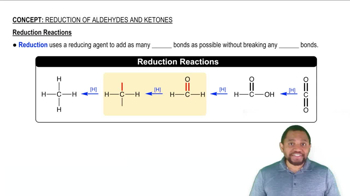


 2:38m
2:38mMaster Reduction Reactions Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning