Consider the following portion of mRNA produced by the normal order of DNA nucleotides:
5'CUU|AAA|CGA|GUU3'
e. What happens to the protein sequence if an A is added to the beginning of the chain and the sequence changes to 5'ACU|UAA|ACG|AGU3'?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: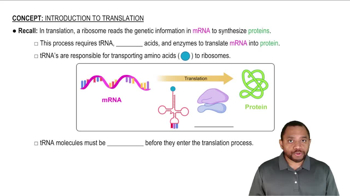


 2:42m
2:42mMaster Translation: Protein Synthesis Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning