Suppose a mutation occurs in the DNA section in problem 17.89, and the first base in the parent chain, adenine, is replaced by guanine.
d. What effect, if any, might this mutation have on the structure and/or function of the resulting protein?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: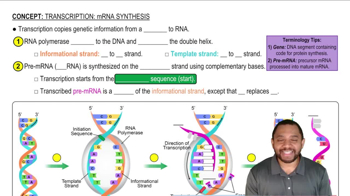


 2:42m
2:42mMaster Translation: Protein Synthesis Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning