Textbook Question
Refer to the diagram of the citric acid cycle in Figure 18.13 to answer each of the following:
b. What are the four-carbon compounds?
556
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

Refer to the diagram of the citric acid cycle in Figure 18.13 to answer each of the following:
b. What are the four-carbon compounds?
Refer to the diagram of the citric acid cycle in Figure 18.13 to answer each of the following:
d. In which reactions are secondary alcohols oxidized?
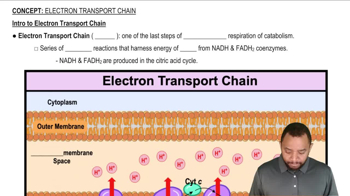
What happens to the energy level as electrons are passed along in electron transport?
How is the H+ gradient established?
How are glycolysis and the citric acid cycle linked to the production of ATP by electron transport?
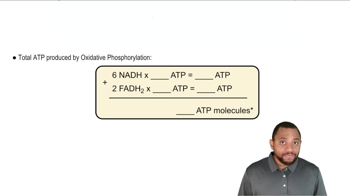
What is the ATP energy yield associated with each of the following?
a. NADH → NAD+