Textbook Question
If there are no reactions in the citric acid cycle that use oxygen, O2, why does the cycle operate only in aerobic conditions?
697
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
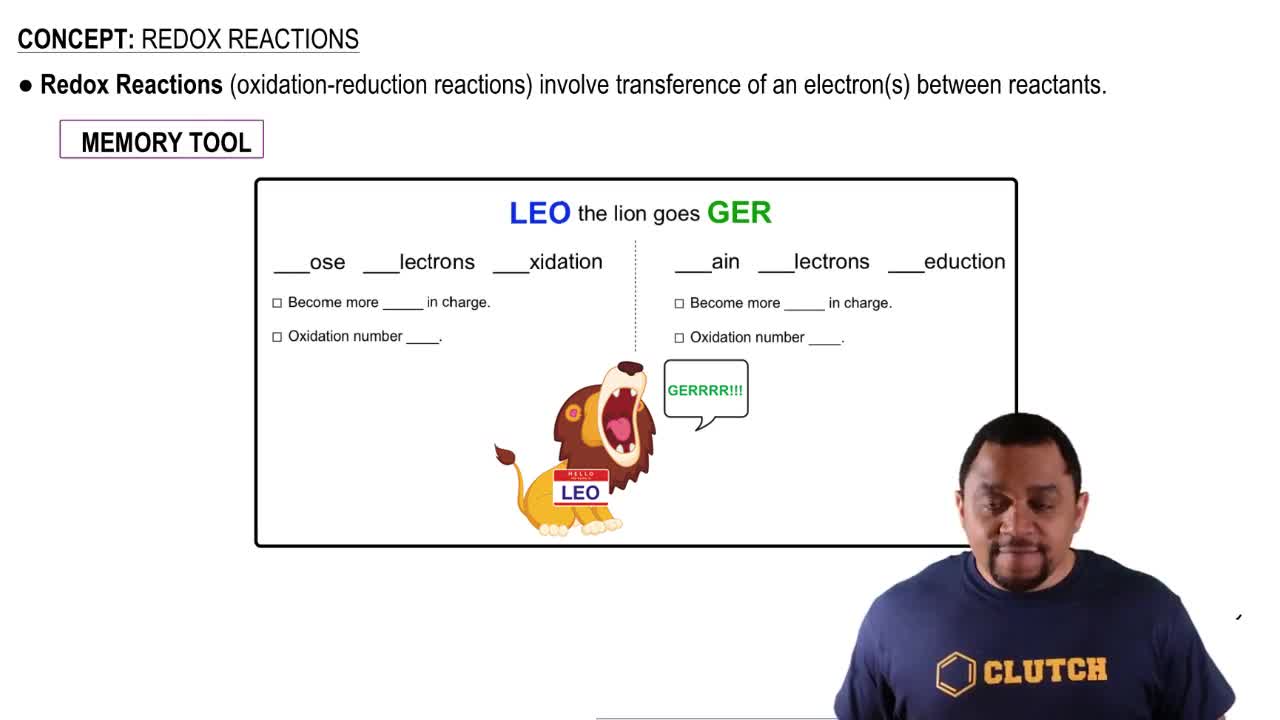

If there are no reactions in the citric acid cycle that use oxygen, O2, why does the cycle operate only in aerobic conditions?
Identify the following as the reduced or oxidized form:
a. NAD+
Identify the following as the reduced or oxidized form:
c. QH2
Mammals can regulate their body heat through a process called thermogenesis. What part of metabolism changes to allow for the production of heat?
What is the effect of proton accumulation in the intermembrane space?
How many ATP are produced when glucose is oxidized to pyruvate compared to when glucose is oxidized to CO2 and H2O?