Textbook Question
How is NADH oxidized in electron transport?
1848
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: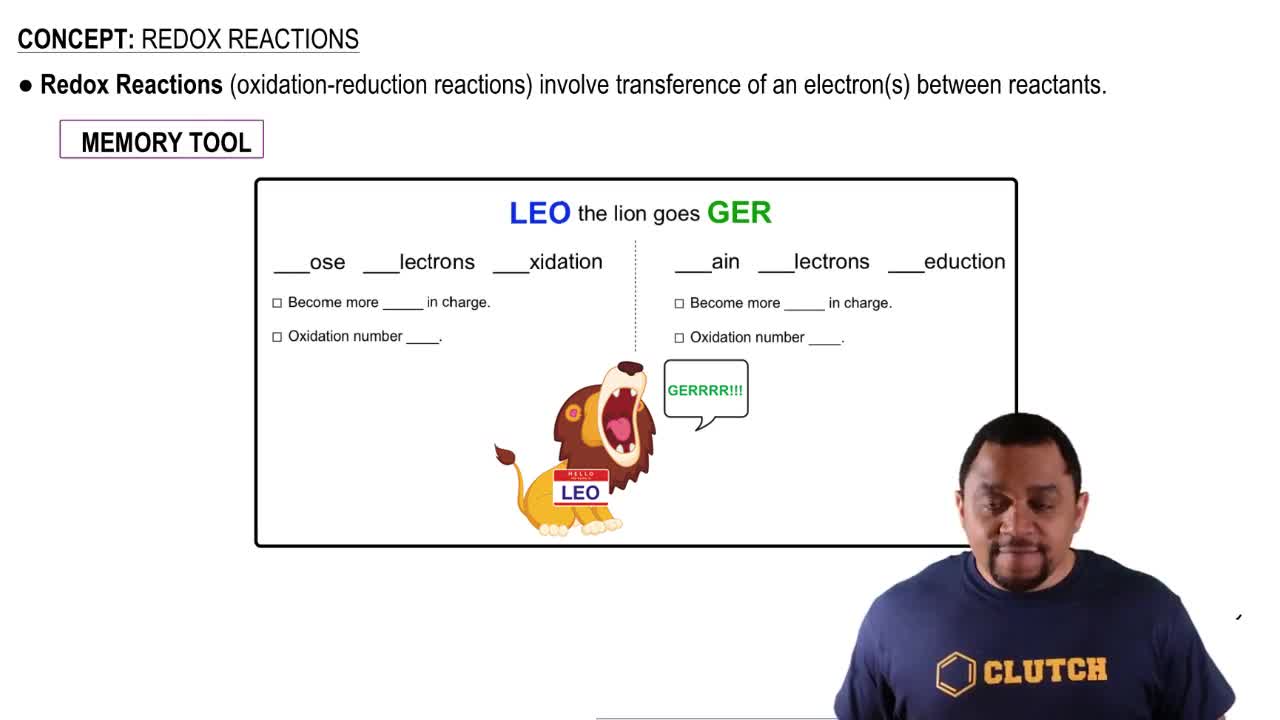



 3:1m
3:1mMaster Intro to Electron Transport Chain Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning