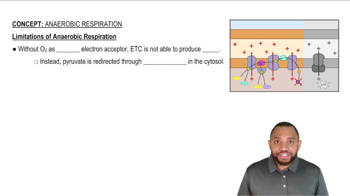
Textbook Question
Complete the following statements:
b. The elements in Group 7A (17) are called the _____.
46
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
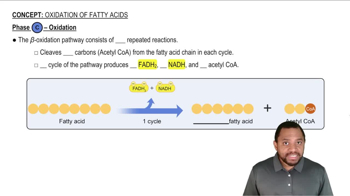

Complete the following statements:
b. The elements in Group 7A (17) are called the _____.
Complete the following statements:
c. Elements that are shiny and conduct heat are called _____.
Indicate if each of the following statements is true or false:
c. The atomic mass unit is based on a carbon atom with six protons and six neutrons.
Indicate if each of the following statements is true or false:
d. The proton and the electron have about the same mass.
Write the name and symbol of the element with the following atomic number:
h. 92