The glycerol derived from lipolysis of triacylglycerols is converted into glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate, which then enters into step 6 of the glycolysis pathway. What further transformations are necessary to convert glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate into pyruvate?
Ch.24 Lipid Metabolism

Chapter 24, Problem 44
How many moles of ATP are produced by the complete oxidation of 1 mol of myristic acid?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the problem: Myristic acid is a saturated fatty acid with the chemical formula C14H28O2. The complete oxidation of fatty acids involves beta-oxidation, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation to produce ATP.
Determine the number of beta-oxidation cycles: Each cycle of beta-oxidation shortens the fatty acid chain by 2 carbons, producing 1 FADH2, 1 NADH, and 1 acetyl-CoA. For myristic acid (14 carbons), the number of beta-oxidation cycles is (14/2) - 1 = 6 cycles.
Calculate the ATP yield from beta-oxidation: Each beta-oxidation cycle produces 1 FADH2 (1.5 ATP) and 1 NADH (2.5 ATP). Multiply these values by the number of cycles (6) to find the total ATP from beta-oxidation.
Determine the ATP yield from acetyl-CoA: Each acetyl-CoA enters the citric acid cycle, producing 3 NADH (7.5 ATP), 1 FADH2 (1.5 ATP), and 1 GTP (1 ATP). For myristic acid, 7 acetyl-CoA molecules are produced (one from each beta-oxidation cycle and one from the final 2-carbon fragment). Multiply these values by 7 to find the total ATP from acetyl-CoA.
Account for the energy cost of activation: The activation of myristic acid to form acyl-CoA requires 2 ATP. Subtract this value from the total ATP calculated in the previous steps to find the net ATP yield from the complete oxidation of 1 mol of myristic acid.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Beta-Oxidation
Beta-oxidation is the metabolic process by which fatty acids are broken down in the mitochondria to generate acetyl-CoA. Each cycle of beta-oxidation shortens the fatty acid chain by two carbon atoms, producing one molecule of acetyl-CoA, which then enters the citric acid cycle for further energy extraction.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Beta Decay Example 1
Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs Cycle)
The citric acid cycle is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA. Each turn of the cycle produces ATP, NADH, and FADH2, which are crucial for the electron transport chain, ultimately leading to the production of additional ATP.
Recommended video:
Guided course
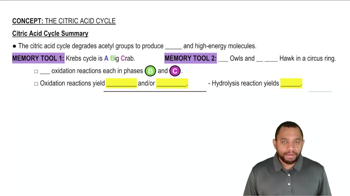
Citric Acid Cycle Summary Concept 12
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation is the final stage of cellular respiration, occurring in the inner mitochondrial membrane. It involves the transfer of electrons through the electron transport chain, creating a proton gradient that drives ATP synthesis via ATP synthase. This process is responsible for producing the majority of ATP during the complete oxidation of fatty acids.
Recommended video:
Guided course
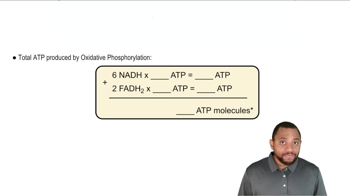
Oxidative Phosphorylation Concept 2
Related Practice
Textbook Question
693
views
Textbook Question
How many molecules of acetyl-CoA result from catabolism of 1 molecule of glyceryl trilaurate?
499
views
Textbook Question
Why is the stepwise oxidation of fatty acids called β oxidation?
1174
views
Textbook Question
Arrange these following four molecules in increasing order of their biological energy content (per mole):
a. Sucrose
b. Myristic acid, CH3(CH2)12COOH
c. Glucose
d. Capric acid, CH3(CH2)8COOH
599
views
Textbook Question
Show the products of each step in the fatty acid oxidation of hexanoic acid.
a.
Textbook Question
Write the equation for the final step in the catabolism of any fatty acid with an even number of carbons.
651
views
