Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
tRNA (Transfer RNA)
tRNA, or transfer RNA, is a type of RNA molecule that plays a crucial role in protein synthesis. It transports specific amino acids to the ribosome, where proteins are assembled. Each tRNA molecule has an anticodon that pairs with a corresponding codon on the mRNA, ensuring that the correct amino acid is added to the growing polypeptide chain.
Recommended video:
rRNA (Ribosomal RNA)
rRNA, or ribosomal RNA, is a fundamental component of ribosomes, the cellular machinery responsible for protein synthesis. It helps to form the structure of ribosomes and catalyzes the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids. rRNA ensures the proper alignment of mRNA and tRNA during translation, facilitating the accurate synthesis of proteins.
Recommended video:
mRNA (Messenger RNA)
mRNA, or messenger RNA, is a type of RNA that carries genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where proteins are synthesized. It is transcribed from DNA and contains codons that specify the sequence of amino acids in a protein. mRNA serves as a template for translation, guiding the assembly of amino acids into polypeptides based on the genetic code.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: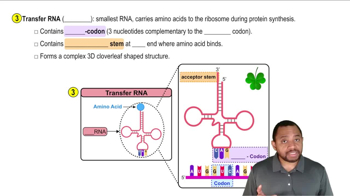



 2:43m
2:43m