Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
tRNA Structure
Transfer RNA (tRNA) is a small RNA molecule that plays a crucial role in protein synthesis. It typically has a cloverleaf shape, which consists of three main loops and an acceptor stem. The structure allows tRNA to carry specific amino acids to the ribosome, where proteins are assembled according to the genetic code.
Recommended video:
Structural Formula Concept 2
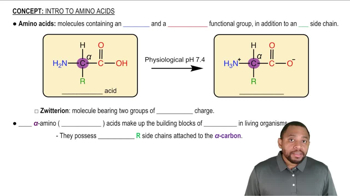
Amino Acid Attachment
Each tRNA molecule is linked to a specific amino acid at its 3' end, which is essential for translation. The attachment occurs through an ester bond formed by the enzyme aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase. This specificity ensures that the correct amino acid is incorporated into the growing polypeptide chain during protein synthesis.
Recommended video:
Intro to Amino Acids Concept 1
Anticodon Function
The anticodon is a sequence of three nucleotides on the tRNA that is complementary to the codon on the mRNA. This pairing is critical for ensuring that the correct amino acid is added to the polypeptide chain. The interaction between the anticodon and codon is a key step in the translation process, facilitating the accurate decoding of genetic information.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 2:43m
2:43m