Textbook Question
Compare the Lewis structures of CH4 and H2O Why do these molecules have similar bond angles but different molecular shapes?
1405
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

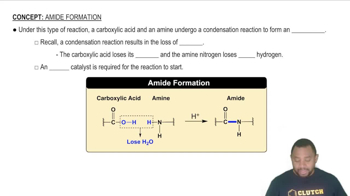

Compare the Lewis structures of CH4 and H2O Why do these molecules have similar bond angles but different molecular shapes?
Why is CCl4 a nonpolar molecule, but is PCl3 a polar molecule?
Identify the major type of intermolecular forces between the particles of each of the following:
b. MgF2
What noble gas has the same electron arrangement as the magnesium ion?
Why are Group 1A (1) and Group 2A (2) elements found in many compounds, but not Group 8A (18) elements?
Consider the following Lewis symbols for elements X and Y:
b. Will a compound of X and Y be ionic or molecular?