For each of the following, give the monosaccharide units produced by hydrolysis, the type of glycosidic bond, and the name of the disaccharide, including α or β:
a.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: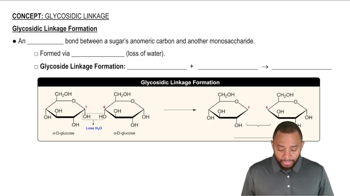



 3:39m
3:39mMaster Types of Disaccharides Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning