Textbook Question
Where do dietary proteins undergo digestion in the body?
1096
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Where do dietary proteins undergo digestion in the body?
What are the end products of the digestion of proteins?
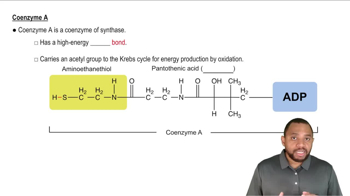
Identify one or more coenzymes with each of the following components:
a. pantothenic acid
What coenzyme picks up hydrogen when a carbon–carbon double bond is formed?
Why is ATP considered an energy-rich compound?
How is ATP used in the initial steps of glycolysis?