The equation for the formation of silicon tetrachloride from silicon and chlorine is Si(s) + 2Cl2(g) → SiCl4(g) + 657 kJ
b. Is the energy of the product higher or lower than the energy of the reactants?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: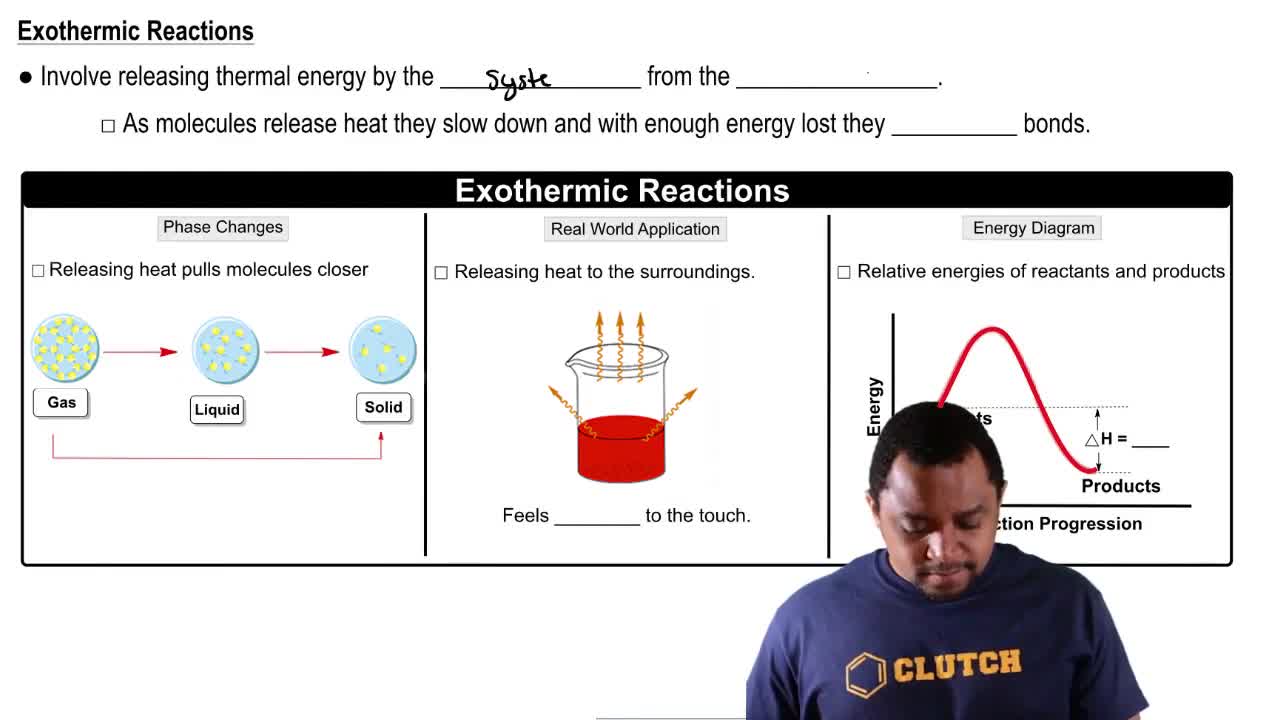



 2:30m
2:30mMaster Endothermic & Exothermic Reactions with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning