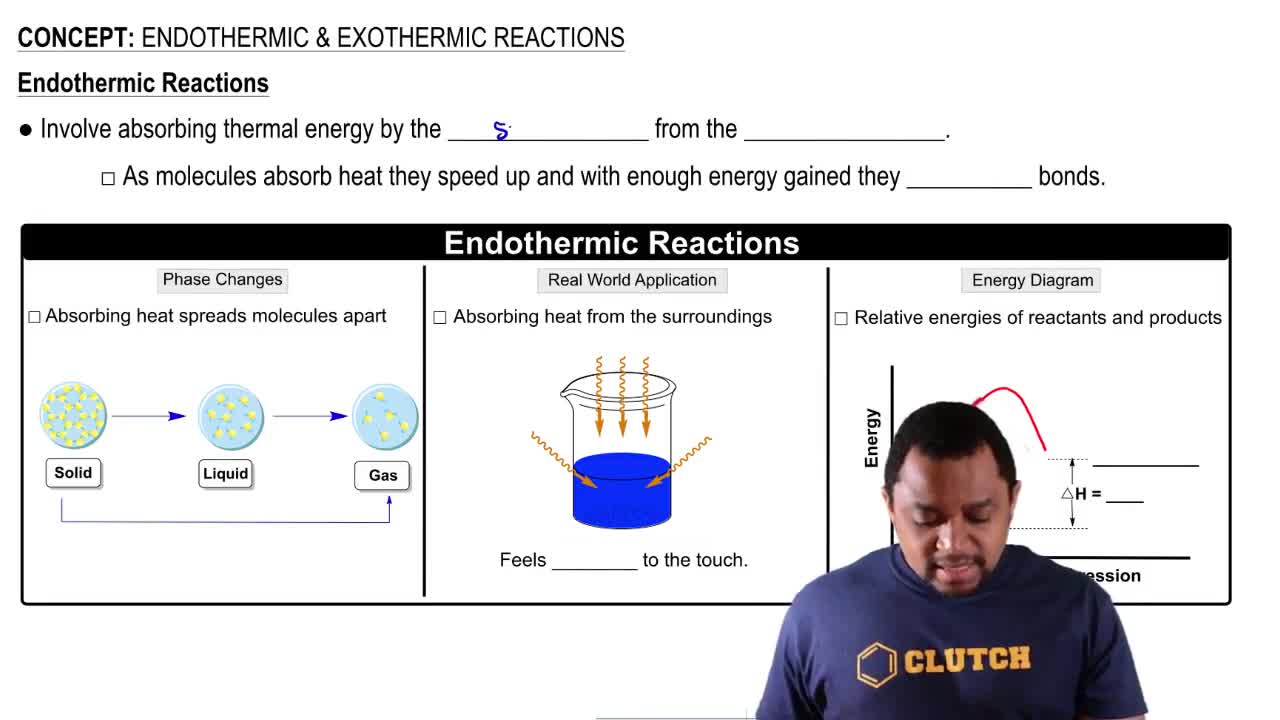
The vaporization of Br2 from the liquid to the gas state requires 7.4 kcal/mol (31.0 kJ/mol).
a. What is the sign of ∆H for this process? Write a reaction showing heat as a product or reactant.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: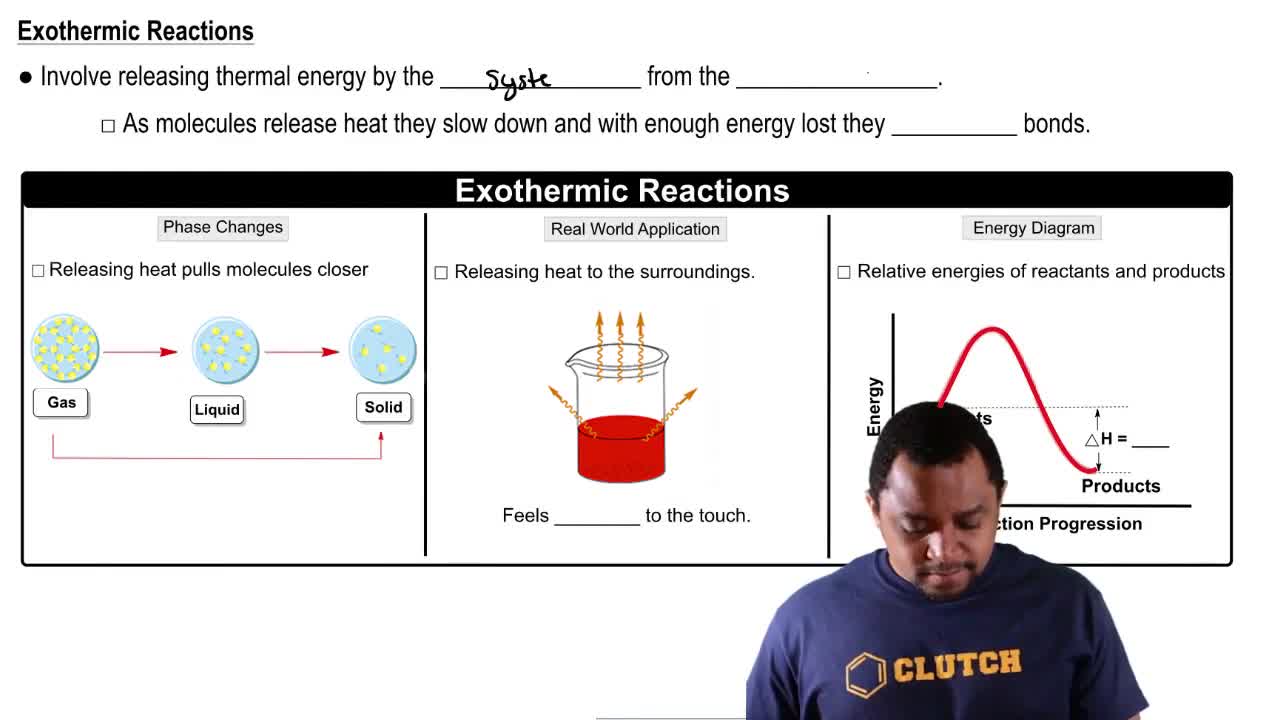


 2:30m
2:30mMaster Endothermic & Exothermic Reactions with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning