What carboxylic acids and amines result from hydrolysis of the following amides?
a.
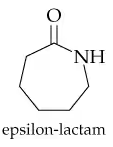
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 1:12m
1:12mMaster Acidic Hydrolysis Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning