Textbook Question
Identify each of the following as a purine or a pyrimidine and name them.
b.
803
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
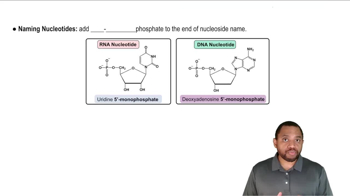

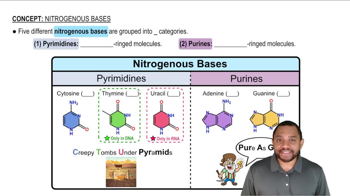
Identify each of the following as a purine or a pyrimidine and name them.
b.
Identify each of the following as a purine or a pyrimidine:
a. guanine
What is the difference between ribose and deoxyribose?
Provide the products for each of the following condensation reactions:
a.
Provide the products for each of the following condensation reactions:
a.
Provide the products for each of the following condensation reactions:
b.