Textbook Question
What happens to the energy level as electrons are passed along in electron transport?
1332
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: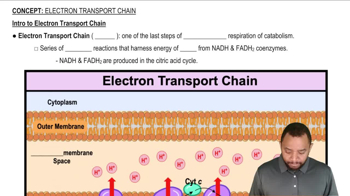


 3:1m
3:1mMaster Intro to Electron Transport Chain Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning