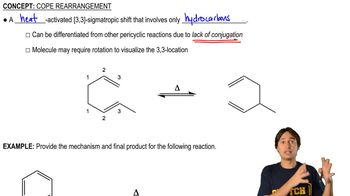
For each synthesis, start with bromocyclohexane and predict the products. Assume that an excess of each reactant is added so that all possible reactions that can happen will happen.
(c)
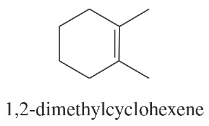
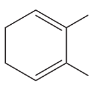
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: