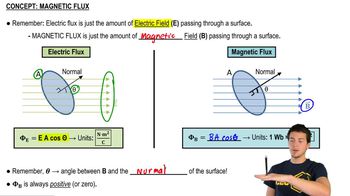
The magnetic field B at all points within the colored circle shown in Fig. E29.15 has an initial magnitude of 0.750 T. (The circle could represent approximately the space inside a long, thin solenoid.) The magnetic field is directed into the plane of the diagram and is decreasing at the rate of -0.0350 T/s. If the ring is cut at some point and the ends are separated slightly, what will be the emf between the ends?
<Image>