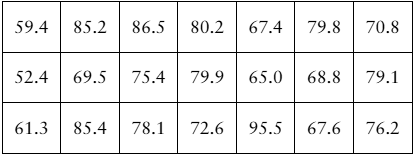
In Exercises 9–12, construct the indicated confidence intervals for (a) the population variance and (b) the population standard deviation . Assume the sample is from a normally distributed population.
c = 0.99, s^2 = 0.64, n = 7
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:



 5:45m
5:45mMaster Constructing Confidence Intervals for Proportions with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learning