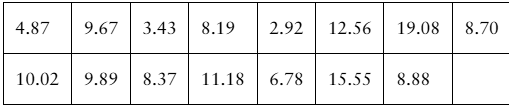
Translating Statements In Exercises 29–34, translate the statement into a confidence interval. Approximate the level of confidence.
In a survey of 2094 U.S. adults who have used an online dating app, 57% said their personal experience with online dating was positive. The survey’s margin of error is ±3.6%. (Source: Pew Research Center)