Describe the hypotheses for a two-way ANOVA test.
Table of contents
- 1. Intro to Stats and Collecting Data1h 14m
- 2. Describing Data with Tables and Graphs1h 56m
- 3. Describing Data Numerically2h 5m
- 4. Probability2h 16m
- 5. Binomial Distribution & Discrete Random Variables3h 6m
- 6. Normal Distribution and Continuous Random Variables2h 11m
- 7. Sampling Distributions & Confidence Intervals: Mean3h 23m
- Sampling Distribution of the Sample Mean and Central Limit Theorem19m
- Distribution of Sample Mean - Excel23m
- Introduction to Confidence Intervals15m
- Confidence Intervals for Population Mean1h 18m
- Determining the Minimum Sample Size Required12m
- Finding Probabilities and T Critical Values - Excel28m
- Confidence Intervals for Population Means - Excel25m
- 8. Sampling Distributions & Confidence Intervals: Proportion2h 10m
- 9. Hypothesis Testing for One Sample5h 8m
- Steps in Hypothesis Testing1h 6m
- Performing Hypothesis Tests: Means1h 4m
- Hypothesis Testing: Means - Excel42m
- Performing Hypothesis Tests: Proportions37m
- Hypothesis Testing: Proportions - Excel27m
- Performing Hypothesis Tests: Variance12m
- Critical Values and Rejection Regions28m
- Link Between Confidence Intervals and Hypothesis Testing12m
- Type I & Type II Errors16m
- 10. Hypothesis Testing for Two Samples5h 37m
- Two Proportions1h 13m
- Two Proportions Hypothesis Test - Excel28m
- Two Means - Unknown, Unequal Variance1h 3m
- Two Means - Unknown Variances Hypothesis Test - Excel12m
- Two Means - Unknown, Equal Variance15m
- Two Means - Unknown, Equal Variances Hypothesis Test - Excel9m
- Two Means - Known Variance12m
- Two Means - Sigma Known Hypothesis Test - Excel21m
- Two Means - Matched Pairs (Dependent Samples)42m
- Matched Pairs Hypothesis Test - Excel12m
- Two Variances and F Distribution29m
- Two Variances - Graphing Calculator16m
- 11. Correlation1h 24m
- 12. Regression3h 33m
- Linear Regression & Least Squares Method26m
- Residuals12m
- Coefficient of Determination12m
- Regression Line Equation and Coefficient of Determination - Excel8m
- Finding Residuals and Creating Residual Plots - Excel11m
- Inferences for Slope31m
- Enabling Data Analysis Toolpak1m
- Regression Readout of the Data Analysis Toolpak - Excel21m
- Prediction Intervals13m
- Prediction Intervals - Excel19m
- Multiple Regression - Excel29m
- Quadratic Regression15m
- Quadratic Regression - Excel10m
- 13. Chi-Square Tests & Goodness of Fit2h 21m
- 14. ANOVA2h 28m
14. ANOVA
Introduction to ANOVA
Problem 10.4.18
Textbook Question
"Using Technology to Perform a Two-Way ANOVA Test In Exercises 15–18, use technology and the block design to perform a two-way ANOVA test. Use α=0.10. Interpret the results. Assume the samples are random and independent, the populations are normally distributed, and the population variances are equal.
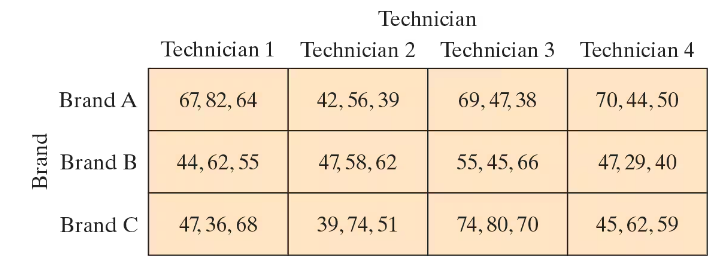
[APPLET] Laptop Repairs The manager of a computer repair service wants to determine whether there is a difference in the time it takes four technicians to repair different brands of laptops. The block design shows the times (in minutes) it took for each technician to repair three laptops of each brand.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Organize the data into a two-way ANOVA format. The rows represent the laptop brands (Brand A, Brand B, Brand C), and the columns represent the technicians (Technician 1, Technician 2, Technician 3, Technician 4). Each cell contains the repair times for the respective brand and technician.
Step 2: Calculate the mean repair time for each brand (row means) and each technician (column means). This helps to understand the overall trends in the data.
Step 3: Use technology (e.g., statistical software or a calculator) to compute the sum of squares for the factors (brands and technicians), the interaction between the factors, and the error term. These values are necessary for the ANOVA table.
Step 4: Construct the ANOVA table, including the degrees of freedom, sum of squares, mean squares, F-statistic, and p-value for each factor (brands and technicians) and their interaction. Use α=0.10 as the significance level.
Step 5: Interpret the results. Compare the p-values for the factors and their interaction to α=0.10. If the p-value is less than α, conclude that there is a significant difference for that factor or interaction. Otherwise, conclude that there is no significant difference.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Two-Way ANOVA
Two-Way ANOVA (Analysis of Variance) is a statistical method used to determine the effect of two independent categorical variables on a continuous dependent variable. It helps in assessing whether there are any statistically significant differences between the means of different groups. In this case, the two factors are the technicians and the brands of laptops, and the dependent variable is the time taken for repairs.
Recommended video:

ANOVA Test
Block Design
Block design is an experimental design technique that involves grouping similar experimental units into blocks to reduce variability. In this scenario, each technician represents a block, and the aim is to control for the variability in repair times that may arise from differences among technicians. This design allows for a clearer analysis of the effect of the brands on repair times while accounting for technician differences.
Recommended video:

Critical Values: t-Distribution
Assumptions of ANOVA
ANOVA relies on several key assumptions: the samples must be independent, the populations should be normally distributed, and the population variances should be equal (homogeneity of variance). In this exercise, these assumptions are crucial for the validity of the test results. If these assumptions are violated, the results of the ANOVA may not be reliable, leading to incorrect conclusions about the differences in repair times.
Recommended video:

ANOVA Test

 6:46m
6:46mWatch next
Master Introduction to ANOVA with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
85
views
