Textbook Question
Most of the CO2 from cellular respiration is released duringa. stage 1: glycolysis.b. stage 2: pyruvate oxidation.c. stage 2: the citric acid cycle.d. stage 3: oxidative phosphorylation.
3026
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: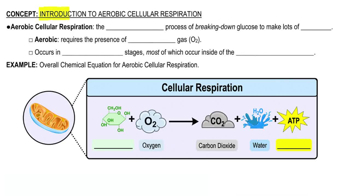



 7:51m
7:51mMaster Review of Aerobic Cellular Respiration with a bite sized video explanation from Bruce Bryan
Start learning