Textbook Question
Fill in the blanks in this summary map to help you review the key concepts of cellular respiration.
2518
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: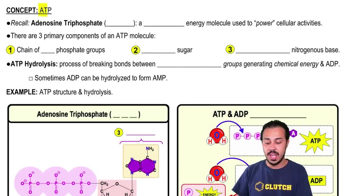



 7:51m
7:51mMaster Review of Aerobic Cellular Respiration with a bite sized video explanation from Bruce Bryan
Start learning