Textbook Question
After glucose is fully oxidized by glycolysis, pyruvate processing, and the citric acid cycle, where is most of its energy stored?
1211
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance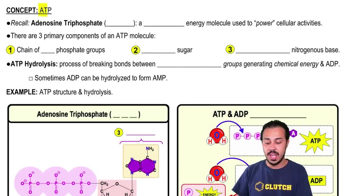

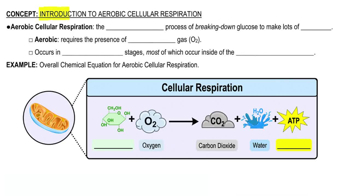

 7:51m
7:51mMaster Review of Aerobic Cellular Respiration with a bite sized video explanation from Bruce Bryan
Start learning