Multiple Choice
A gram of fat oxidized by respiration produces approximately twice as much ATP as a gram of carbohydrate. Which of the following best explains this observation?
2903
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: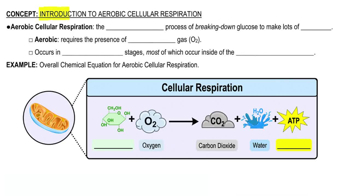
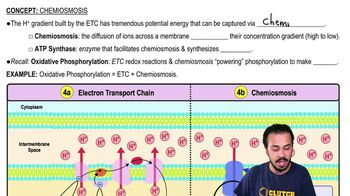


 7:51m
7:51mMaster Review of Aerobic Cellular Respiration with a bite sized video explanation from Bruce Bryan
Start learning