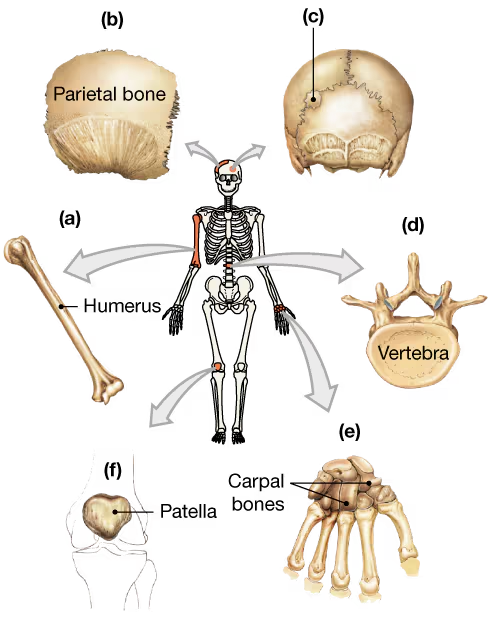
Multiple Choice
Which of the following bones is accurately described as an irregular bone?
191
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 2:58m
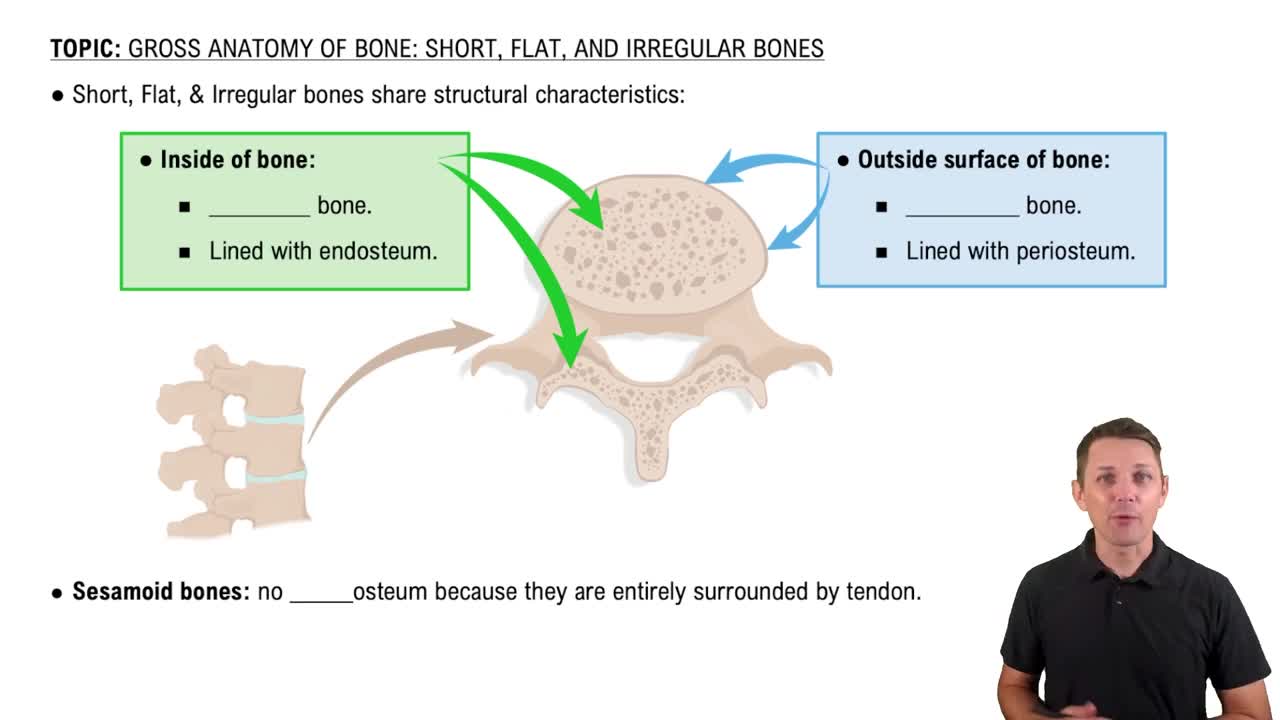
2:58mMaster Short, Flat, and Irregular Bones with a bite sized video explanation from Bruce Bryan
Start learning