
 Taylor, Simon, Dickey, Hogan 10th Edition
Taylor, Simon, Dickey, Hogan 10th Edition Ch. 16 Microbial Life: Prokaryotes and Protists
Ch. 16 Microbial Life: Prokaryotes and Protists Problem 4
Problem 4A new organism has been discovered. Tests have revealed that it is unicellular, is autotrophic, and has a cell wall that contains peptidoglycan. Based on this evidence, it should be classified as a(n)
a. Alga.
b. Archaean.
c. Protist.
d. Bacterium.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
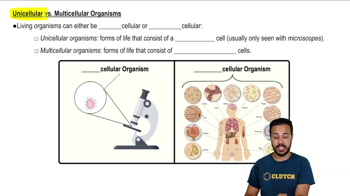
Unicellularity
Autotrophy

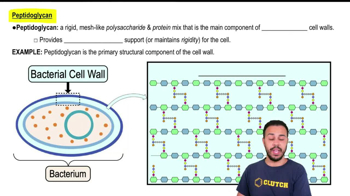
Peptidoglycan in Cell Walls
Fill in the blanks on the phylogenetic tree (on the facing page) to show current hypotheses for the origin of multicellular organisms.
In terms of nutrition, autotrophs are to heterotrophs as
a. Kelp are to diatoms.
b. Archaea are to bacteria.
c. Slime molds are to algae.
d. Algae are to slime molds.
Which pair of protists has support structures composed of silica?
a. Dinoflagellates and diatoms
b. Diatoms and radiolarians
c. Radiolarians and forams
d. Forams and amoebozoans
Which of the following members of the SAR supergroup is incorrectly paired with its clade?
a. Stramenopiles—brown algae
b. Alveolates—parasites such as Plasmodium
c. Alveolates—dinoflagellates
d. Rhizaria—diatoms
Which of the following prokaryotes is not pathogenic?
a. Chlamydia
b. Rhizobium
c. Streptococcus
d. Salmonella