Back
BackProblem 53
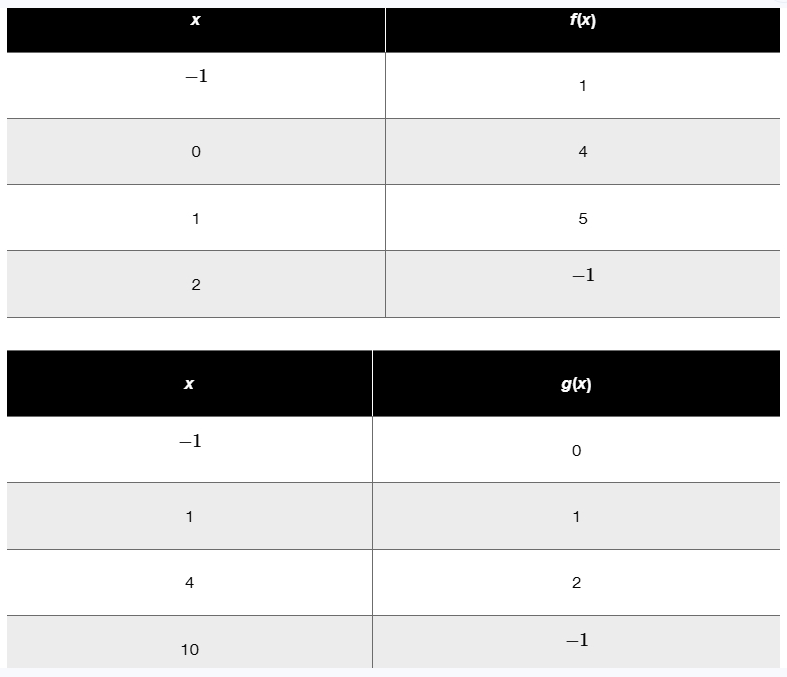
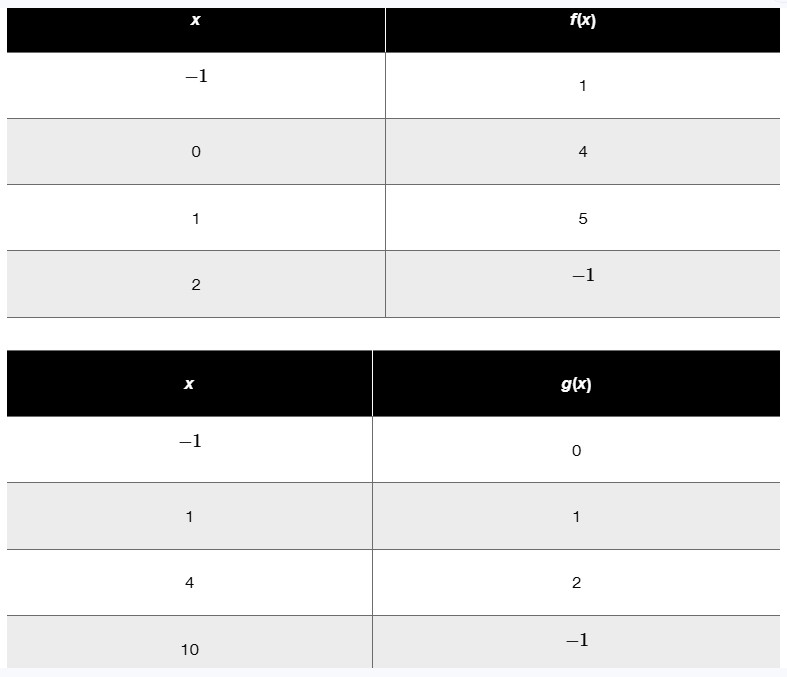
In Exercises 53–58, f and g are defined by the following tables. Use the tables to evaluate each composite function. f(g(1))
Problem 55
In Exercises 53–58, f and g are defined by the following tables. Use the tables to evaluate each composite function. (go f) (-1)
Problem 59
Let f(x) = 2x - 5 g(x) = 4x - 1 h(x) = x² + x + 2. Evaluate the indicated function without finding an equation for the function. (fog) (0)
Problem 61
Let f(x) = 2x - 5 g(x) = 4x - 1 h(x) = x² + x + 2. Evaluate the indicated function without finding an equation for the function. ƒ-1 (1)
Problem 64
Let f(x) = 2x - 5 g(x) = 4x - 1 h(x) = x² + x + 2. Evaluate the indicated function without finding an equation for the function. f(g[h (1)])
Problem 95
Determine whether each statement is true or false. If the statement is false, make the necessary change(s) to produce a true statement.
If and , find and .
Problem 100
Solve by completing the square: 2x² – 5x + 1 = 0.
Problem 101
Solve: 5x3/4- 15 = 0.
Problem 102
Solve and graph the solution set on a number line: 3|2x-1| ≥ 21
Problem 104
Exercises 103–105 will help you prepare for the material covered in the next section. Use a rectangular coordinate system to graph the circle with center (1, -1) and radius 1.
Problem 105
Exercises 103–105 will help you prepare for the material covered in the next section. Solve by completing the square: y² – 6y — 4 = 0.
Problem 1
Find the distance between each pair of points. If necessary, express answers in simplified radical form and then round to two decimal places. (2, 3) and (14, 8)
Problem 3
Find the distance between each pair of points. If necessary, express answers in simplified radical form and then round to two decimal places. (4, -1) and (-6, 3)
Problem 6
Find the distance between each pair of points. If necessary, express answers in simplified radical form and then round to two decimal places. (0, 0) and (3,-4)
Problem 7
Find the distance between each pair of points. If necessary, express answers in simplified radical form and then round to two decimal places. (-2, -6) and (3, −4)
Problem 11
Find the distance between each pair of points. If necessary, express answers in simplified radical form and then round to two decimal places. (3.5, 8.2) and (-0.5, 6.2)
Problem 13
Find the distance between each pair of points. If necessary, express answers in simplified radical form and then round to two decimal places. (0, −√3) and (√5, 0)
Problem 14
Find the distance between each pair of points. If necessary, express answers in simplified radical form and then round to two decimal places. (0, -√2) and (√7,0)
Problem 15
Find the distance between each pair of points. If necessary, express answers in simplified radical form and then round to two decimal places. (3√3, √5) and (−√3, 4√5)
Problem 17
Find the distance between each pair of points. If necessary, express answers in simplified radical form and then round to two decimal places. (7/3, 1/5) and (1/3, 6/5)
Problem 18
Find the distance between each pair of points. If necessary, express answers in simplified radical form and then round to two decimal places. (-1/4, -1/7) and (3/4, 6/7)
Problem 19
Find the midpoint of each line segment with the given endpoints. (6, 8) and (2, 4)
Problem 21
Find the midpoint of each line segment with the given endpoints. (-2, -8) and (−6, −2)
Problem 23
Find the midpoint of each line segment with the given endpoints. (-3, -4) and (6, −8)
Problem 25
Find the midpoint of each line segment with the given endpoints. (-7/2, 3/2) and (-5/2, -11/2)
Problem 27
Find the midpoint of each line segment with the given endpoints. (8, 3√5) and (−6, 7√5)
Problem 28
Find the midpoint of each line segment with the given endpoints. (7√3, −6) and (3√3, −2)
Problem 31
Write the standard form of the equation of the circle with the given center and radius. Center (0, 0), r = 7
Problem 33
Write the standard form of the equation of the circle with the given center and radius. Center (3, 2), r = 5
Problem 35
Write the standard form of the equation of the circle with the given center and radius. Center (-1, 4), r = 2