 Back
BackProblem 37
Write the standard form of the equation of the circle with the given center and radius. Center (−3, −1), r = √3
Problem 39
Write the standard form of the equation of the circle with the given center and radius. Center (-4, 0), r = 10
Problem 41
Give the center and radius of the circle described by the equation and graph each equation. Use the graph to identify the relation's domain and range. x² + y² = 16
Problem 43
Give the center and radius of the circle described by the equation and graph each equation. Use the graph to identify the relation's domain and range. (x − 3)² + (y + 1)² = 36
Problem 45
Give the center and radius of the circle described by the equation and graph each equation. Use the graph to identify the relation's domain and range. (x+3)² + (y - 2)² = 4
Problem 47
Give the center and radius of the circle described by the equation and graph each equation. Use the graph to identify the relation's domain and range. (x + 2)² + (y + 2)² = 4
Problem 51
Give the center and radius of the circle described by the equation and graph each equation. Use the graph to identify the relation's domain and range. (x + 1)² + y² = 25
Problem 53
Complete the square and write the equation in standard form. Then give the center and radius of each circle and graph the equation. x² + y²+6x+2y+6 = 0
Problem 55
Complete the square and write the equation in standard form. Then give the center and radius of each circle and graph the equation. x² + y² – 10x – 6y – 30 = 0
Problem 57
Complete the square and write the equation in standard form. Then give the center and radius of each circle and graph the equation. x² + y²+8x-2y-8=0
Problem 59
Complete the square and write the equation in standard form. Then give the center and radius of each circle and graph the equation. x² - 2x + y² – 15 = 0
Problem 60
Complete the square and write the equation in standard form. Then give the center and radius of each circle and graph the equation. x² + y² - 6y -7=0
Problem 61
Complete the square and write the equation in standard form. Then give the center and radius of each circle and graph the equation. x² + y² − x + 2y + 1 = 0
Problem 64
Complete the square and write the equation in standard form. Then give the center and radius of each circle and graph the equation. x² + y²+3x+5y+9/4=0
Problem 66
A line segment through the center of each circle intersects the circle at the points shown. a. Find the coordinates of the circle's center. b. Find the radius of the circle. c. Use your answers from parts (a) and (b) to write the standard form of the circle's equation.
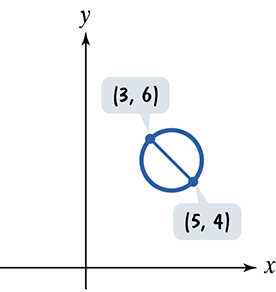
Problem 67
Graph both equations in the same rectangular coordinate system and find all points of intersection. Then show that these ordered pairs satisfy the equations. x² + y² = 16, x-y = 4
Problem 69
Graph both equations in the same rectangular coordinate system and find all points of intersection. Then show that these ordered pairs satisfy the equations. (x − 2)²+(y+3)² = 4, y = x - 3
Problem 55
In Exercises 55–59, use the graph of to graph each function g.
g(x) = f(x + 2) + 3
Problem 62
In Exercises 60–63, begin by graphing the standard quadratic function, f(x) = x2. Then use transformations of this graph to graph the given function. r(x) = -(x + 1)2
Problem 64
In Exercises 64–66, begin by graphing the square root function, f(x) = √x. Then use transformations of this graph to graph the given function. g(x) = √(x + 3)
Problem 66
In Exercises 64–66, begin by graphing the square root function, f(x) = √x. Then use transformations of this graph to graph the given function. r(x) = 2√(x + 2)
Problem 69
In Exercises 67–69, begin by graphing the absolute value function, f(x) = |x|. Then use transformations of this graph to graph the given function. r(x) = (1/2) |x + 2|
Problem 77
Find the domain of each function. g(x) = 4/(x - 7)
Problem 79
Find the domain of each function.
Problem 83
Find f + g, f - g, fg, and f/g. f(x) = x2 + x + 1, g(x) = x2 -1
Problem 87
Find a. (f ○ g)(x); b. the domain of (f ○ g). f(x) = (x + 1)/(x - 2), g(x) = 1/x
Problem 89
Express the given function h as a composition of two functions f and g so that h(x) = (f ○ g)(x). h(x) = (x2 + 2x - 1)4
Problem 93
The functions in Exercises 93–95 are all one-to-one. For each function, (a) find an equation for f-1(x), the inverse function. (b) Verify that your equation is correct by showing that f(f-1(x)) = x and f-1(f(x)) = x. f(x) = 4x - 3

