Reiji and Tuneko Okazaki conducted a now classic experiment in 1968 in which they discovered a population of short fragments synthesized during DNA replication. They introduced a short pulse of ³H-thymidine into a culture of E. coli and extracted DNA from the cells at various intervals. In analyzing the DNA after centrifugation in denaturing gradients, they noticed that as the interval between the time of ³H-thymidine introduction and the time of centrifugation increased, the proportion of short strands decreased and more labeled DNA was found in larger strands. What would account for this observation?
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
8. DNA Replication
Overview of DNA Replication
Problem 36
Textbook Question
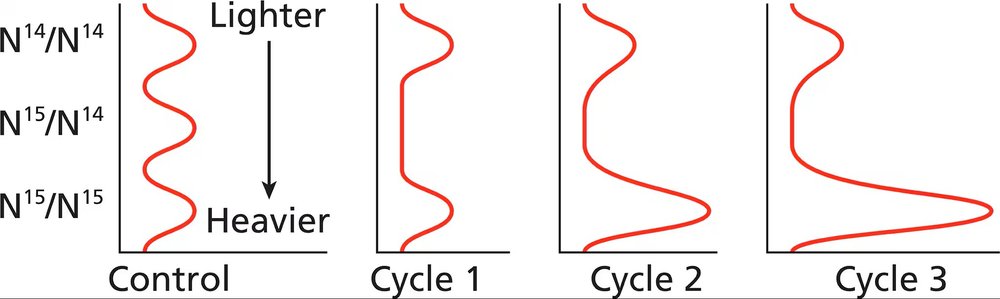
Suppose that future exploration of polar ice on Mars identifies a living microbe and that analysis indicates the organism carries double-stranded DNA as its genetic material. Suppose further that DNA replication analysis is performed by first growing the microbe in a growth medium containing the heavy isotope of nitrogen (¹⁴N) that the organism is then transferred to a growth medium containing the light isotope of nitrogen (¹⁴N) and that the nitrogen composition of the DNA is examined by CsCl ultracentrifugation and densitometry after the first, second, and third replication cycles in the ¹⁴N-containing medium. The results of the experiment are illustrated here for each cycle. The control shows the positioning of the three possible DNA densities. Based on the results shown, what can you conclude about the mechanism of DNA replication in this organism?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Begin by understanding the Meselson and Stahl experiment, which demonstrated the semi-conservative mechanism of DNA replication in E. coli. In semi-conservative replication, each new DNA molecule consists of one original (parental) strand and one newly synthesized strand. This experiment used isotopes of nitrogen (¹⁵N and ¹⁴N) to distinguish between old and new DNA strands based on their density.
Step 2: Analyze the experimental setup described in the problem. The microbe is first grown in a medium containing the heavy isotope of nitrogen (¹⁵N), which incorporates into its DNA, making it denser. Then, the organism is transferred to a medium containing the light isotope of nitrogen (¹⁴N), and DNA replication occurs in this new medium. The density of the DNA is examined after each replication cycle using CsCl ultracentrifugation and densitometry.
Step 3: Interpret the results of the first replication cycle. If the DNA replication is semi-conservative, the DNA molecules will consist of one strand with ¹⁵N (heavy) and one strand with ¹⁴N (light). This hybrid DNA will have an intermediate density between the heavy and light DNA controls.
Step 4: Examine the results of the second replication cycle. In semi-conservative replication, each hybrid DNA molecule will produce two new DNA molecules: one hybrid (intermediate density) and one fully light DNA molecule (light density). This will result in two distinct bands in the densitometry analysis: one at intermediate density and one at light density.
Step 5: Analyze the results of the third replication cycle. With each subsequent cycle, the proportion of fully light DNA molecules increases, while the proportion of hybrid DNA molecules decreases. By the third cycle, the densitometry analysis should show a stronger band at the light density and a weaker band at the intermediate density. This pattern confirms the semi-conservative mechanism of DNA replication in the organism.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
5mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
DNA Replication Mechanisms
DNA replication can occur through three primary mechanisms: conservative, semi-conservative, and dispersive. In conservative replication, the original DNA molecule remains intact, while a completely new copy is made. Semi-conservative replication, which is the mechanism confirmed by the Meselson and Stahl experiment, involves each new DNA molecule consisting of one original strand and one newly synthesized strand. Dispersive replication results in DNA strands that are mixtures of old and new DNA.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Steps to DNA Replication
Meselson and Stahl Experiment
The Meselson and Stahl experiment was a pivotal study that demonstrated the semi-conservative nature of DNA replication. By using isotopes of nitrogen (¹⁵N and ¹⁴N), they were able to track the distribution of DNA strands after several replication cycles. The results showed that after one replication cycle, all DNA had an intermediate density, and after two cycles, there were distinct bands corresponding to both light and hybrid DNA, confirming that each new DNA molecule contained one old and one new strand.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Mendel's Experiments
CsCl Ultracentrifugation
CsCl ultracentrifugation is a technique used to separate DNA based on its density. When DNA is subjected to a high-speed centrifugation in a cesium chloride gradient, the DNA molecules will settle at a position corresponding to their density. This method was crucial in the Meselson and Stahl experiment, as it allowed the researchers to visualize the different densities of DNA after replication, providing clear evidence for the semi-conservative model of DNA replication.
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1226
views


