Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Heterozygosity
Heterozygosity refers to the presence of two different alleles at a specific gene locus on homologous chromosomes. In the context of genetic counseling, a heterozygous individual may carry one normal allele and one mutated or rearranged allele. This genetic variation can sometimes lead to a normal phenotype, especially if the normal allele is sufficient to produce the necessary gene product.
Recommended video:
Chromosomal Rearrangements
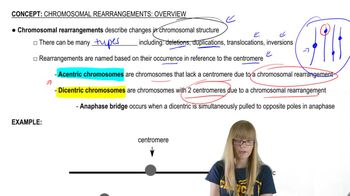
Chromosomal rearrangements involve structural changes to chromosomes, such as deletions, duplications, inversions, or translocations. These alterations can disrupt gene function or regulation, potentially leading to phenotypic changes. However, not all rearrangements result in observable traits, particularly if they do not affect essential genes or if the individual has compensatory mechanisms.
Recommended video:
Phenotypic Expression
Phenotypic expression is the observable physical or biochemical characteristics of an organism, determined by both genetic makeup and environmental influences. In cases of chromosomal rearrangements, phenotypic effects may depend on factors such as the specific genes involved, the nature of the rearrangement, and whether the individual has a second functional copy of the affected gene. Thus, a phenotypically normal individual with a chromosomal rearrangement may not exhibit any traits associated with that rearrangement.
Recommended video:
Penetrance and Expressivity