Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
DNA Structure
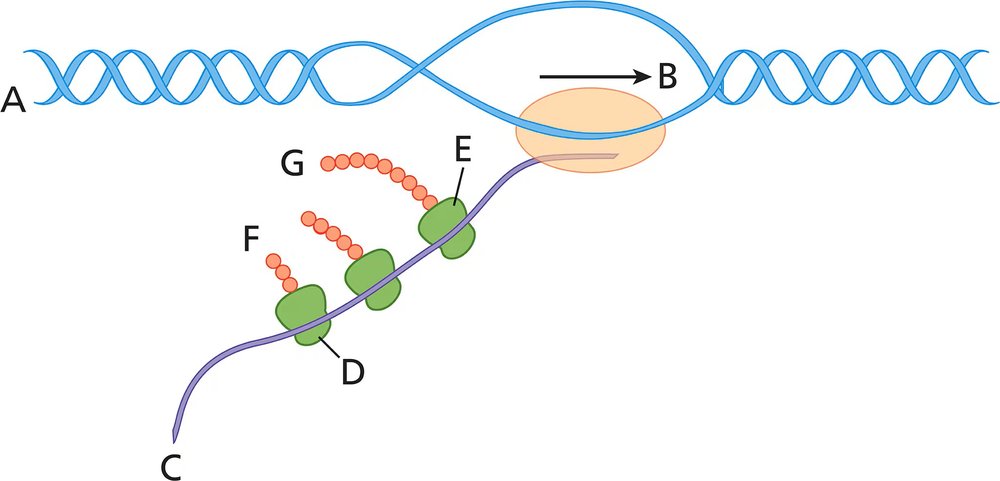
DNA is a double helix composed of two strands running in opposite directions, known as antiparallel strands. Each strand has a 5' (five-prime) end and a 3' (three-prime) end, which are crucial for understanding the directionality of DNA. The 5' end has a phosphate group, while the 3' end has a hydroxyl group, influencing how DNA is replicated and transcribed.
Recommended video:
Nucleotide Orientation
Nucleotides, the building blocks of DNA, are linked together by phosphodiester bonds between the 5' phosphate group of one nucleotide and the 3' hydroxyl group of another. This orientation is essential for understanding how DNA strands are synthesized and how they interact with enzymes during processes like replication and transcription.
Recommended video:
DNA Terminology
In molecular biology, the terms '5' end' and '3' end' are used to describe the orientation of the DNA strands. When analyzing a diagram, identifying which end is labeled as 5' or 3' helps determine the direction of the DNA strand and its relationship to other components, such as genes or regulatory elements, which may be crucial for answering questions about the diagram.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:



 6:32m
6:32m