Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Heritability (H²)
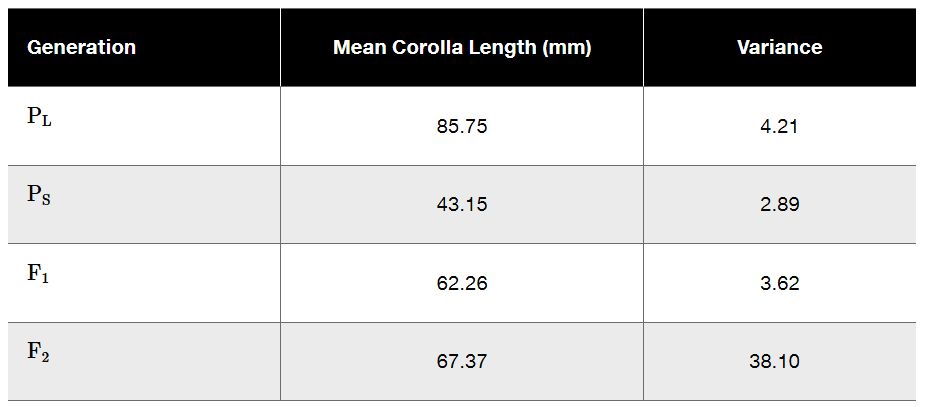
Heritability (H²) is a measure used in genetics to quantify the proportion of phenotypic variance in a trait that can be attributed to genetic variance among individuals in a population. It is calculated using the formula H² = Vg / Vp, where Vg is the genetic variance and Vp is the total phenotypic variance. Understanding heritability helps in predicting how traits may respond to selection and informs breeding strategies.
Recommended video:
Phenotypic Variance (Vp)
Phenotypic variance (Vp) refers to the total variance observed in a trait within a population, which includes both genetic variance (Vg) and environmental variance (Ve). It is essential to distinguish between these components to understand how much of the observed variation is due to genetic differences versus environmental influences. In the context of the question, Vp is derived from the variances of the parental and F1 and F2 generations.
Recommended video:
Genetic Variance (Vg)
Genetic variance (Vg) is the portion of phenotypic variance that is attributable to genetic differences among individuals. It can be further divided into additive genetic variance, dominance variance, and interaction variance. In the context of the Nicotiana example, calculating Vg involves analyzing the differences in mean corolla lengths between the parental strains and their offspring, which helps in understanding the heritable component of the trait.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:



 7:04m
7:04m