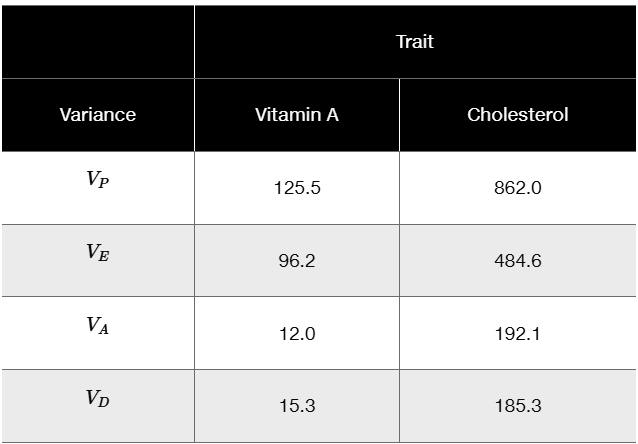
The following variances were calculated for two traits in a herd of hogs.
Calculate broad-sense (H²) and narrow-sense (h²) heritabilities for each trait in this herd.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:



 7:04m
7:04mMaster Calculating Heritability with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia
Start learning