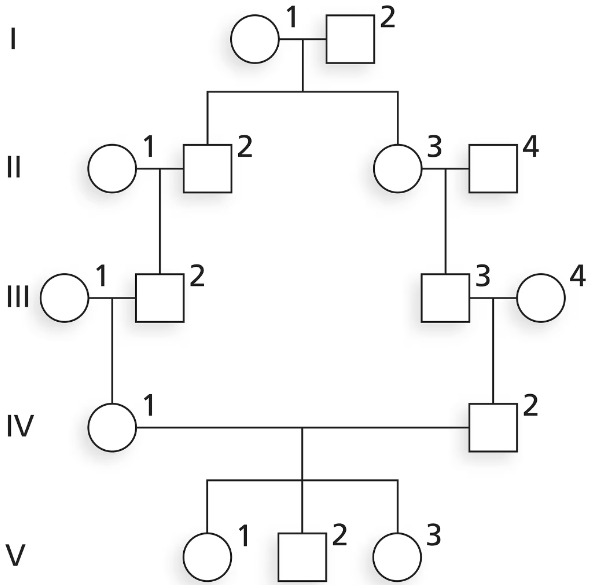
Evaluate the following pedigree, and answer the questions below for individual IV-1. Is IV-1 an inbred individual? If so, who is/are the common ancestor(s)?
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
21. Population Genetics
Allelic Frequency Changes
Problem 34a
Textbook Question
Evaluate the following pedigree, and answer the questions below. Which individual(s) in this family is/are inbred?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand the concept of inbreeding. Inbreeding occurs when individuals who are closely related genetically (e.g., cousins, siblings) reproduce. This increases the likelihood of homozygosity for recessive alleles, which can lead to genetic disorders.
Step 2: Analyze the pedigree chart provided. Look for instances where individuals share common ancestors, indicating a potential inbreeding event. Specifically, trace the lineage of each individual to identify shared ancestry.
Step 3: Focus on the offspring of unions between individuals who are related. In the chart, identify any individuals whose parents are cousins or otherwise closely related.
Step 4: Highlight the individuals who are products of such unions. For example, if two cousins have children, those children are considered inbred because their parents share a common ancestor.
Step 5: Confirm the inbred individuals by verifying the shared ancestry of their parents. Use the pedigree chart to ensure that the parents are indeed related and that the offspring are direct descendants of this union.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Pedigree Analysis
Pedigree analysis is a method used to study the inheritance patterns of traits in families. It involves creating a diagram that represents family relationships and the transmission of genetic traits across generations. By analyzing the pedigree, one can identify carriers of specific traits, determine the mode of inheritance, and assess the likelihood of traits appearing in future generations.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Pedigree Flowchart
Inbreeding
Inbreeding refers to the mating of individuals who are closely related genetically, which can increase the probability of offspring inheriting genetic disorders. In a pedigree, inbreeding is often indicated by a mating between individuals who share a common ancestor. This practice can lead to a higher incidence of homozygous recessive conditions due to the increased likelihood of both parents carrying the same recessive alleles.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Non-Random Mating
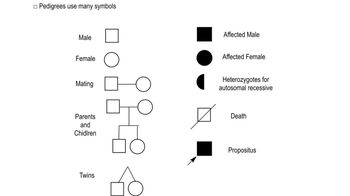
Symbols in Pedigrees
In pedigree charts, specific symbols are used to represent individuals and their relationships. Males are typically represented by squares, while females are represented by circles. A filled symbol indicates an affected individual, while an empty symbol indicates an unaffected individual. Understanding these symbols is crucial for interpreting the pedigree and identifying patterns of inheritance, including potential inbreeding.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Pedigree Symbols
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
384
views


