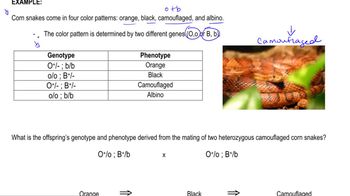
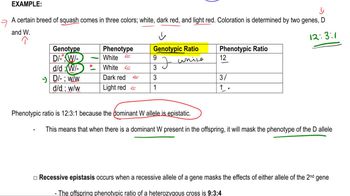
3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance
Epistasis and Complementation
3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance
Epistasis and Complementation
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
When performing a complementation test, how do you know if two mutations complement?
963views1rank - Multiple Choice
How can you tell if two genes are epistatic?
1023views1rank1comments - Multiple Choice
Two heterozygous organisms are crossed, and the F2 phenotypic ratio is 12:3:1. What form of epistasis do these two genes exhibit?
782views1rank - Multiple Choice
A cross of white plants and red plants was performed. Using the F2 phenotypic ratio data below, determine what form of gene interaction is taking place.
598views3rank