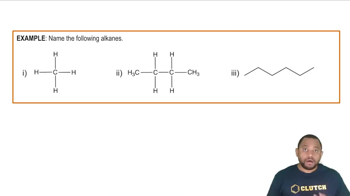
When pentane is exposed to Br2 in the presence of light, a halogenation reaction occurs. Write the formulas of:
a. All possible products containing only one bromine
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 2:39m
2:39mMaster Rules for Naming Alkanes Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning