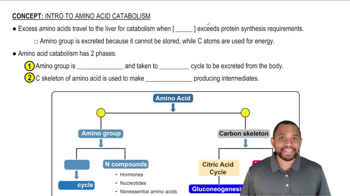
What metabolic substrate(s) are produced from the carbon atoms of each of the following amino acids?
b. asparagine
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 2:41m
2:41mMaster Amino Acid Catabolism: Carbon Atoms Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning