Textbook Question
Draw the Fischer projection for the enantiomer (mirror image) of each of the following:
(a)
578
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

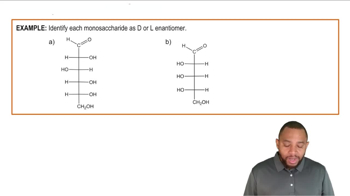

Draw the Fischer projection for the enantiomer (mirror image) of each of the following:
(a)
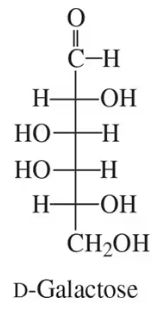
Classify structures A, B, and C in the figure as being either an enantiomer or a diastereomer of D-galactose.
Use the structure of D-galactose in Problem 6.15 to answer the following:
(a) Draw the Fischer projection of the carbon 3 epimer.
Identify the monosaccharide that fits each of the following descriptions:
(a) also referred to as dextrose
Identify the monosaccharide that fits each of the following descriptions:
(a) in combination with glucose produces the disaccharide lactose
Indicate whether the following statements apply to type 1 or type 2 diabetes:
(a) most cases begin in youth