Convert the following models into line drawings and identify the functional groups in each:
b.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: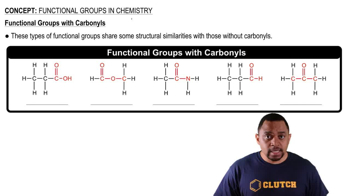



 2:14m
2:14mMaster Hydrocarbons Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning