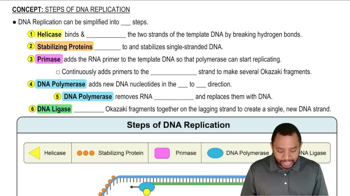
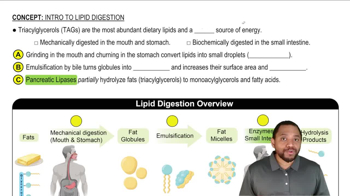
Match the type of radiation (1 to 3) with each of the following statements:
1. alpha particle
2. beta particle
3. gamma radiation
c. travels only a short distance in air
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 2:06m
2:06mMaster Types of Radiation Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning