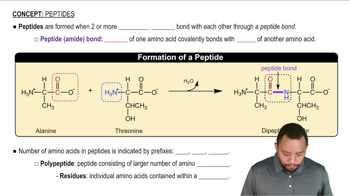
Peptides isolated from rapeseed that may lower blood pressure have the following sequence of amino acids. Draw the structure for each peptide and write the one-letter abbreviations.
a. Arg–Ile–Tyr
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: