Hydrogen chloride can be made from the reaction of chlorine and hydrogen:
Cl2(g) + H2(g) → 2 HCl(g)
For this reaction, K = 26 × 1033 and ∆H = -44 kcal/mol(-184 kJ/mol) at 25 °C.
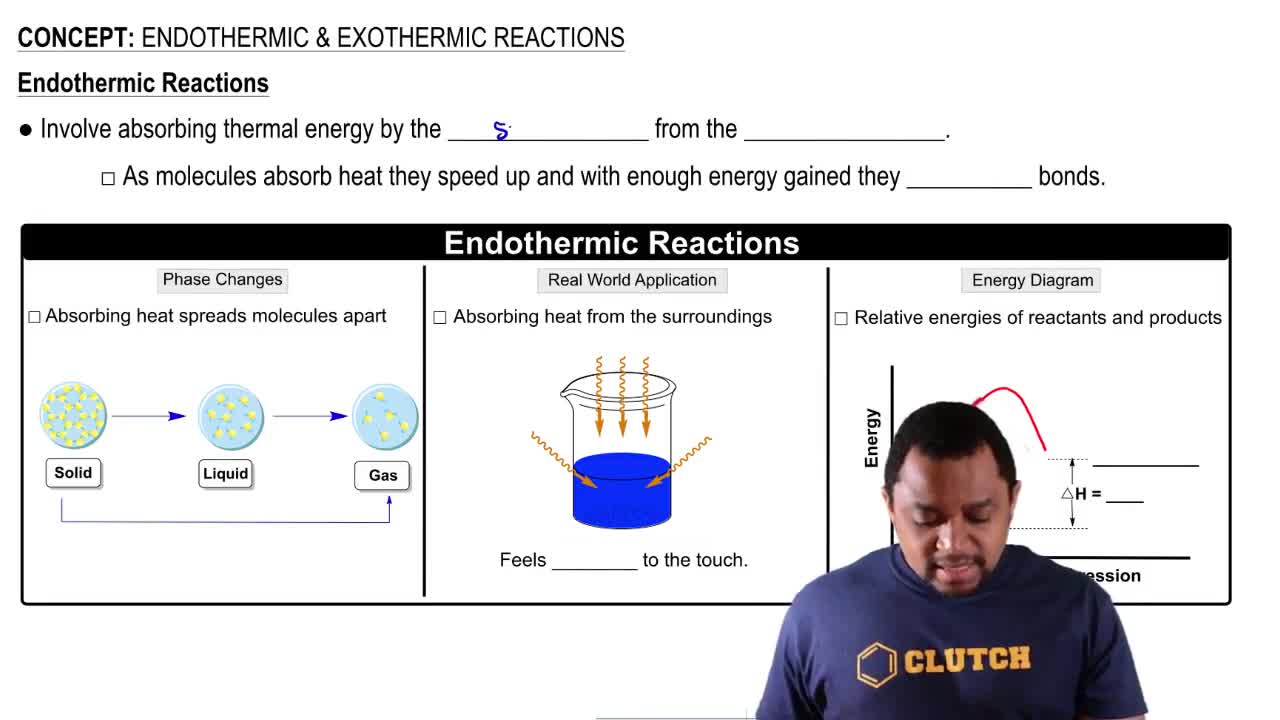
a. Is the reaction endothermic or exothermic?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: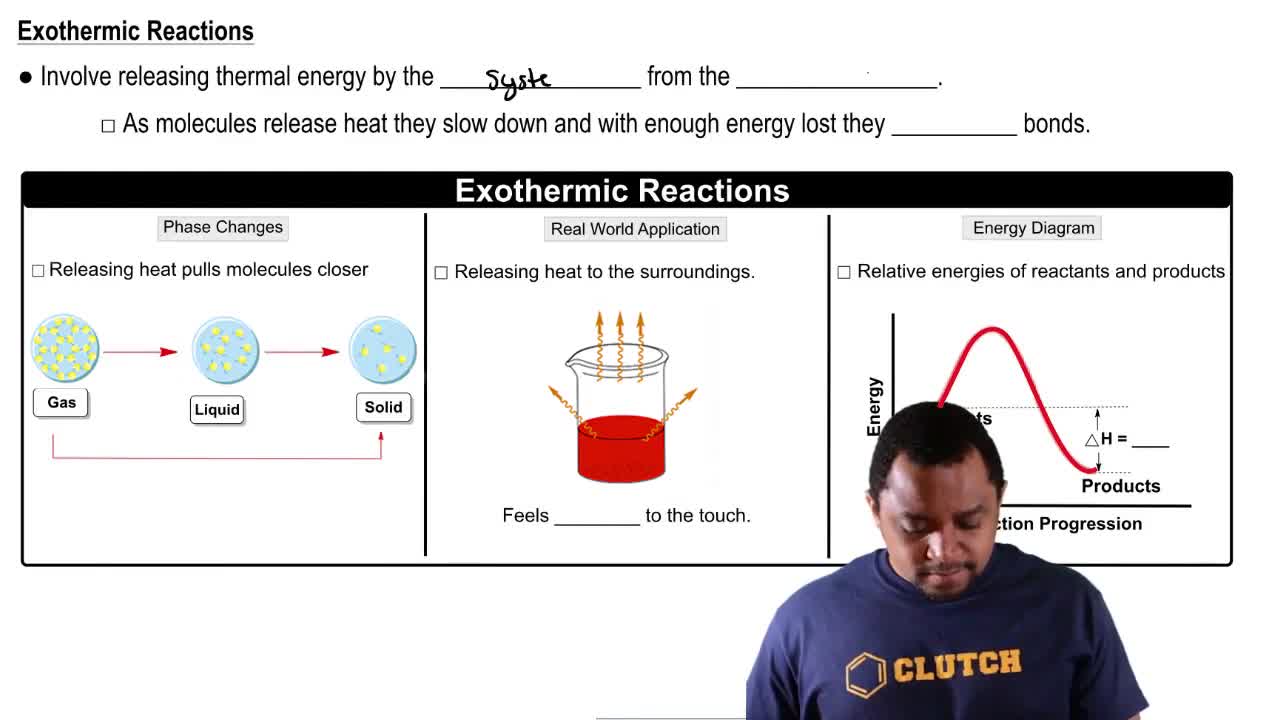


 2:30m
2:30mMaster Endothermic & Exothermic Reactions with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning