Textbook Question
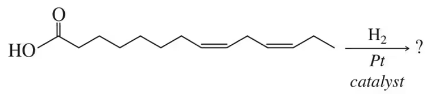
Write the products of the following reactions:
(a)
650
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



Write the products of the following reactions:
(a)
Fill in the missing organic products or reactants for the following hydrogenation reactions:
(a)
Epinephrine is the active ingredient in the EpiPen® used to treat severe allergic reactions. EpiPens expire due to the oxidation of the epinephrine. One of these reactions is shown below. Circle the groups in the product that were oxidized.
Fill in the missing organic products for the complete hydrogenation of the following:
(c)
Fill in the missing organic product or reactant for the following hydration reactions:
(b)
Fill in the missing organic product or reactant for the following hydration reactions:
(a)