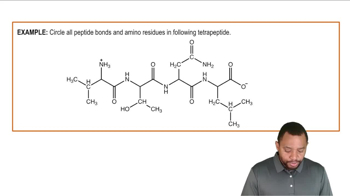
Tuftsin is an immunostimulator tetrapeptide having the following sequence:
Thr–Lys–Pro–Arg
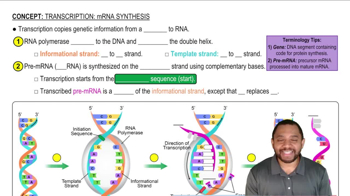
Write a possible sequence for the gene (Informational & template strand) that codes for this tetrapeptide.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 2:42m
2:42mMaster Translation: Protein Synthesis Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning