Alkynes undergo hydrogenation to give alkanes, just as alkenes do. Draw and name the products that would result from hydrogenation of the alkynes shown in Problem 13.25.
<IMAGE>
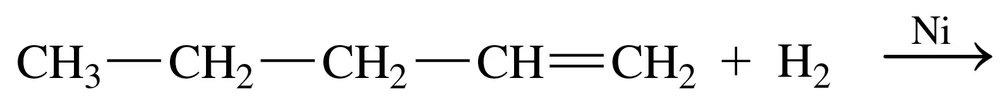
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:



 1:22m
1:22mMaster Hydrogenation Reactions Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning