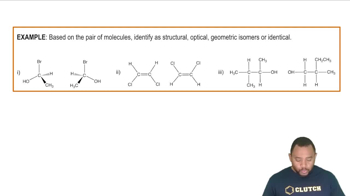
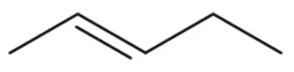
For each of the following compounds, indicate whether or not it can exist as cis–trans stereoisomers. If it can exist as the two isomers, draw both as a condensed structure.
(a) H2C=CHCH2CH3
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: