Textbook Question
Draw a structure for a compound that meets each of the following descriptions:
b. An 8-carbon ketone with six carbons as its longest chain
914
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
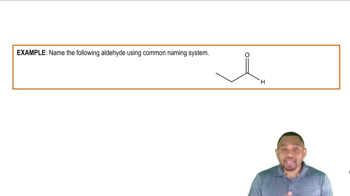
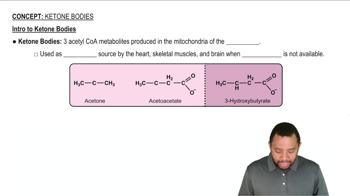
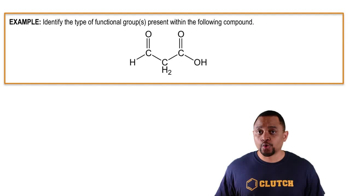
Draw a structure for a compound that meets each of the following descriptions:
b. An 8-carbon ketone with six carbons as its longest chain
Draw a structure for a compound that meets each of the following descriptions:
d. A cyclic alpha-hydroxyketone, C5H8O2
Indicate which compounds contain aldehyde or ketone carbonyl groups.
a.
Indicate which compounds contain aldehyde or ketone carbonyl groups.
f.
Redraw each of the following in line structure format. Indicate which compounds have an aldehyde carbonyl group, a ketone carbonyl group, or neither.
c.
Redraw each of the following in line structure format. Indicate which compounds have an aldehyde carbonyl group, a ketone carbonyl group, or neither.
e. CH3CH2COCH2CH3